Overview
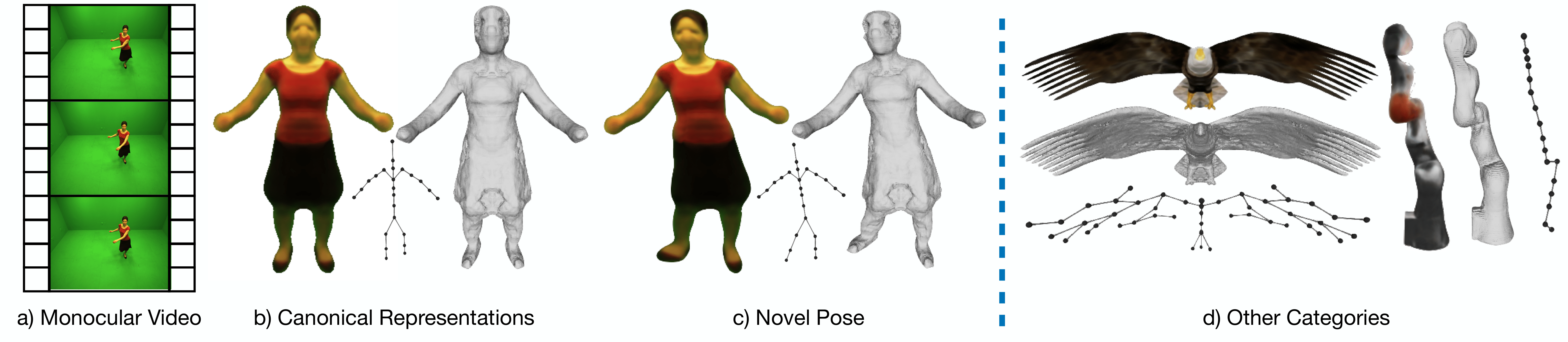
Given monocular videos of an articulated object, our method builds its canonical representation, including 3D shape, appearance, and a corresponding animatable 3D kinematic chain for direct pose manipulations. Our approach does not rely on any information on the object's shape and underlying structure. In c) we show example of re-posing the human in b) to novel pose. We show the learned canonical representations of other object categories in d).
Abstract
Animating an object in 3D often requires an articulated structure, e.g. a kinematic chain or skeleton of the manipulated object with proper skinning weights, to obtain smooth movements and surface deformations. However, existing models that allow direct pose manipulations are either limited to specific object categories or built with specialized equipment. To reduce the work needed for creating animatable 3D models, we propose a novel reconstruction method that learns an animatable kinematic chain for any articulated object. Our method operates on monocular videos without prior knowledge of the object's shape or underlying structure. Our approach is on par with state-of-the-art 3D surface reconstruction methods on various articulated object categories while enabling direct pose manipulations by re-posing the learned kinematic chain.
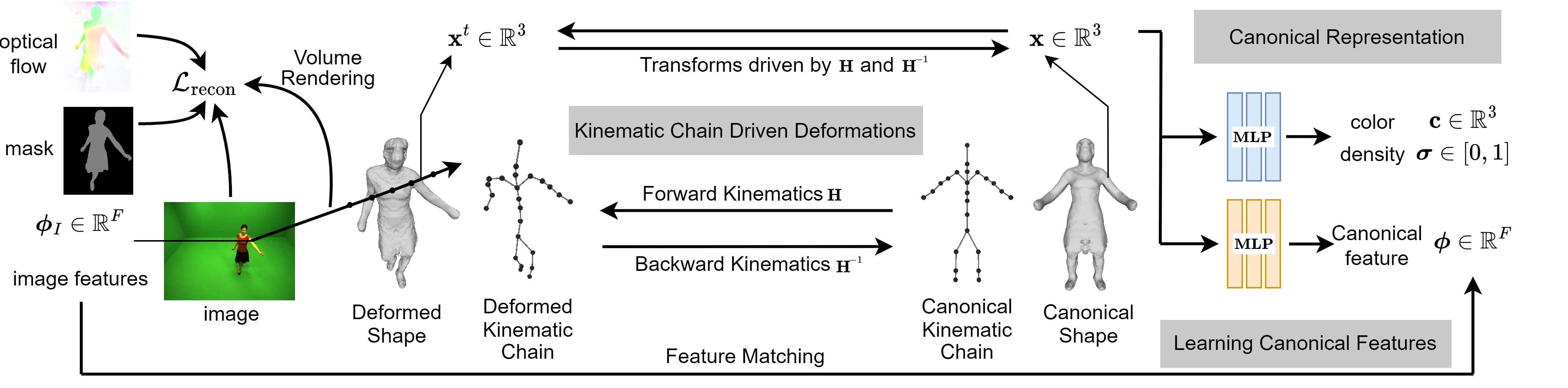
Our Pipeline

Our method optimizes the canonical representation, including the object's shape, appearance, and kinematic chain, to enable direct pose manipulations. It uses the kinematic chain to transform 3D points between the canonical and deformed space, and render 2D observation predictions of colors, foreground masks and optical flows to match the actual 2D observations. In addition, canonical feature embeddings are learned by matching the corresponding 2D image features to establish the object parts level correspondences across different frames within a collection of monocular videos.
3D Reconstruction Results
Here we show the 3D reconstruction results of the frames in input videos for different objects:
Kinematic Chain Driven Re-posing
Here we show the results of re-posing the meshes by directly manipulating the learned kinematic chains for different objects:
Sample Videos from Our iiwa Robotic Arm Dataset
In addition to the monocular videos of the iiwa robotic arm, we provide ground-truth 3D mesh, segmentation mask, and camera pose for each frame of the videos. Our dataset can be accessed and downloaded from here.